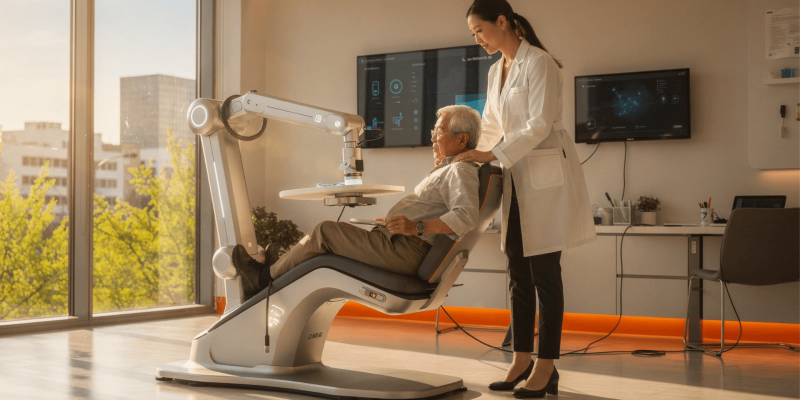
AI in physiotherapy is no longer a distant concept discussed only in research papers or conferences. It is already influencing day-to-day clinical practice across healthcare.
From supporting clinical decision-making to enabling remote monitoring and reducing administrative workload, AI is reshaping how care is delivered and physiotherapy is no exception.
As digital tools continue to evolve, an important question emerges for physiotherapists:
How can AI in physiotherapy be integrated in a way that enhances clinical practice, protects patient trust, and improves rehabilitation outcomes?
This article explores the real-world opportunities and challenges of AI in physiotherapy, grounded in clinical evidence, ethical considerations, and the realities of modern practice.
What AI in Physiotherapy Really Means
AI refers to computer systems that can identify patterns, analyse data, and generate evidence-based recommendations.
In physiotherapy, this does not mean replacing clinical reasoning. Instead, AI acts as a supportive tool that enhances professional expertise and expands the scope of care.
Key areas where AI is already making a measurable impact include:
1. AI-Driven Clinical Decision Support
Consider assessing a patient following a complex knee injury. Alongside your physical examination and clinical judgement, an AI-enabled tool analyses thousands of anonymised recovery profiles.
It highlights that this patient’s age, strength deficits, and functional scores may increase the risk of delayed recovery.
AI does not make the decision, but supports it.
Machine-learning models are increasingly effective in predicting:
-
Re-injury risk
-
Expected recovery timelines
-
Barriers to rehabilitation engagement
This enables faster, more confident, and data-informed clinical decision-making.
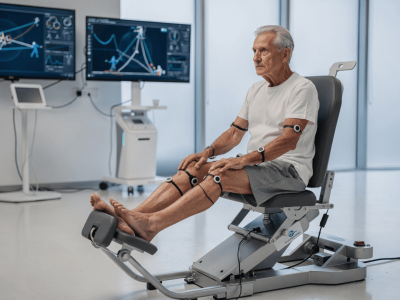
2. Movement Analysis and Remote Rehabilitation Monitoring
Traditionally, advanced movement analysis required expensive biomechanics laboratories. Today, computer vision and smartphone-based AI tools allow clinicians to access:
-
Joint angle measurement
-
Detection of compensatory movement patterns
-
Movement deviation alerts
-
Real-time exercise feedback
Leading digital musculoskeletal (MSK) platforms now support high-quality remote rehabilitation.
For example, an ACL reconstruction patient performing home exercises can receive immediate form correction while clinicians monitor adherence and movement quality between sessions.
This elevates hybrid and remote physiotherapy from convenience to clinical effectiveness.
3. AI-Supported Documentation and Clinical Notes
Documentation remains one of the most time-intensive aspects of physiotherapy practice. Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools, including AI clinical scribes, can now:
-
Transcribe patient consultations
-
Summarise key clinical findings
-
Generate draft clinical notes
-
Reduce administrative workload
Early adoption studies show clinicians saving significant time per consultation, allowing more focus on patient care rather than paperwork.
4. Personalised Rehabilitation Through Predictive Insights
AI’s strength lies in its ability to analyse large datasets and identify trends that may not be immediately visible. In physiotherapy, this enables:
-
Prediction of rehabilitation dropout risk
-
Estimation of post-surgical recovery timelines
-
Early identification of patients at risk of slower progress
-
More precise exercise progression planning
In neurorehabilitation and MSK care, predictive platforms are already helping clinicians adjust treatment plans proactively rather than reactively.
Benefits: Why Physiotherapists Should Pay Attention
When implemented ethically and thoughtfully, AI in physiotherapy can:
-
Improve efficiency by automating repetitive tasks
-
Increase accuracy through objective movement analysis
-
Enhance personalisation via predictive modelling
-
Expand access to care through hybrid and remote pathways
-
Boost patient engagement, with evidence showing improved home-exercise adherence
These benefits are already being observed in real-world digital health environments.
Challenges: Why Critical Evaluation Matters
Despite its potential, AI in physiotherapy adoption must be approached carefully.
1. Data Quality and Bias
If AI systems are trained on non-diverse or incomplete datasets, their predictions may not generalise to all populations, risking inequitable care.
2. Over-Reliance on Technology
AI should never override a physiotherapist’s expertise. Clinical reasoning, contextual judgement, and patient interaction remain central to effective rehabilitation.
3. Ethical and Legal Responsibilities
Key considerations include:
-
Data privacy and GDPR compliance
-
Secure data storage
-
Informed patient consent
-
Transparency in how AI systems function
4. Patient Trust and Perception
Some patients may worry that technology reduces human connection. Clear communication is essential to reinforce that AI supports not replaces, the therapeutic relationship.
The World Health Organization (2021) emphasises that AI in healthcare must be guided by strong ethical principles and clinician oversight.
The Future of Physiotherapy: A Hybrid Model
AI will not replace physiotherapists but it will reshape how physiotherapy is delivered.
The future points toward:
-
Adaptive rehabilitation pathways driven by real-time data
-
Early identification of risks to prevent setbacks
-
Expanded clinician reach through remote monitoring
-
Reduced administrative burden
-
Greater focus on clinical reasoning and patient connection
This transformation is already underway.
Final Thoughts: AI as a Clinical Partner, Not a Replacement
AI is neither a cure-all nor a threat to physiotherapy. It is a powerful tool when used responsibly and limited when applied uncritically.
For physiotherapists, the opportunity lies in engaging early, shaping ethical implementation, and ensuring that patient-centred care remains at the core of rehabilitation.
As the saying goes: “AI doesn’t replace clinicians, it augments them.”
In physiotherapy, that means enhancing what we already do best: helping people move better, recover faster, and live healthier lives.